How to operate a drone is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from safety protocols and legal regulations to troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly and confidently.
We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, explaining their functions and how they interact to enable flight. Then, we’ll guide you through a step-by-step process for safe takeoff and landing, introducing various techniques for different situations. Mastering flight controls, understanding camera settings for optimal image quality, and adhering to relevant regulations are also key aspects we’ll thoroughly address.
Finally, we’ll provide practical troubleshooting advice to help you navigate common problems and maintain your drone’s peak performance.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will Artikel the key parts of a typical drone, providing a glossary of common terms and a comparison of propeller types.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. Let’s explore each one:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust, efficiency, and noise.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Their speed and direction are controlled by the flight controller.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this onboard computer processes sensor data and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It integrates data from various sensors like the accelerometer, gyroscope, and barometer.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power to the motors and other components. Battery life is a critical factor in flight duration and range.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Allows the drone to determine its location and maintain position, crucial for features like autonomous flight and return-to-home (RTH).
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. The quality and features of the camera vary widely depending on the drone model.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology is essential for understanding manuals, troubleshooting issues, and communicating effectively with other drone enthusiasts.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller)
- Regulates the speed of the motors.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit)
- Measures the drone’s orientation and movement using accelerometers and gyroscopes.
- RTH (Return to Home)
- A feature that allows the drone to automatically return to its starting point.
- VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing)
- Ability to take off and land vertically.
- Gimbal
- A stabilized mount for the camera, minimizing image shake.
Drone Propeller Comparison

Different propellers are designed for specific purposes. The choice of propeller can significantly impact flight performance.
| Propeller Type | Pitch | Diameter | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow-spinning | Low | Large | High lift, low speed, quieter |
| Fast-spinning | High | Small | High speed, lower lift, noisier |
| Standard | Medium | Medium | Balance of speed and lift |
| Carbon Fiber | Variable | Variable | Lightweight, durable, high performance |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This section details essential steps, hazard identification, and emergency procedures.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, diligently follow this checklist:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is properly connected.
- Verify GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (if necessary).
- Confirm the controller is properly paired with the drone.
- Check the weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation).
- Review local regulations and restrictions on drone operation.
- Identify potential hazards in the flight area (obstacles, people, animals).
Hazard Identification and Mitigation
Identifying and mitigating potential hazards is crucial for preventing accidents. Always be aware of your surroundings and potential risks such as:
- Obstacles (buildings, trees, power lines)
- People and animals
- Weather conditions (strong winds, rain)
- Radio frequency interference
- Loss of signal
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is essential for safe drone operation. In case of:
- Battery failure: Immediately initiate RTH (Return to Home) if available. If not, attempt a controlled descent to the nearest safe area.
- Loss of signal: Most drones have an RTH function that will automatically return the drone to its starting point. If this fails, visually locate the drone and attempt to regain control.
Safe Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight inspection process:
1. Inspect Drone for Damage → 2. Check Battery Level and Connection → 3. Verify GPS Signal → 4. Calibrate Sensors (if needed) → 5.
Pair Controller → 6. Check Weather → 7. Review Regulations → 8. Identify Hazards → Ready for Flight
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and understanding of its controls; for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both the pilot and the surrounding environment.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are essential for preventing accidents. This section Artikels procedures and techniques.
Step-by-Step Takeoff Procedure
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal lock.
- Calibrate the compass (if needed).
- Slowly increase throttle to lift off vertically.
- Hover at a safe altitude before proceeding with flight.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Different techniques exist for takeoff and landing, including:
- Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL): The drone takes off and lands straight up and down, ideal for confined spaces.
- Horizontal Takeoff and Landing: The drone takes off and lands like an airplane, requiring more space.
Altitude Control During Takeoff and Landing
Maintaining controlled altitude is crucial. Methods include:
- Using the throttle control to adjust ascent and descent rate.
- Utilizing altitude hold features (if available).
Common Takeoff and Landing Errors and Solutions

- Problem: Drone tilting during takeoff. Solution: Ensure proper calibration and check for uneven propeller balance.
- Problem: Drifting during hover. Solution: Recalibrate the compass and check for wind conditions.
- Problem: Rough landing. Solution: Practice smooth throttle control and use landing gear if available.
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding drone flight controls is fundamental for safe and effective operation. This section covers basic and advanced maneuvers.
Basic Flight Controls
Most drones use a control stick configuration. The primary controls are:
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up/down).
- Pitch: Controls forward/backward movement.
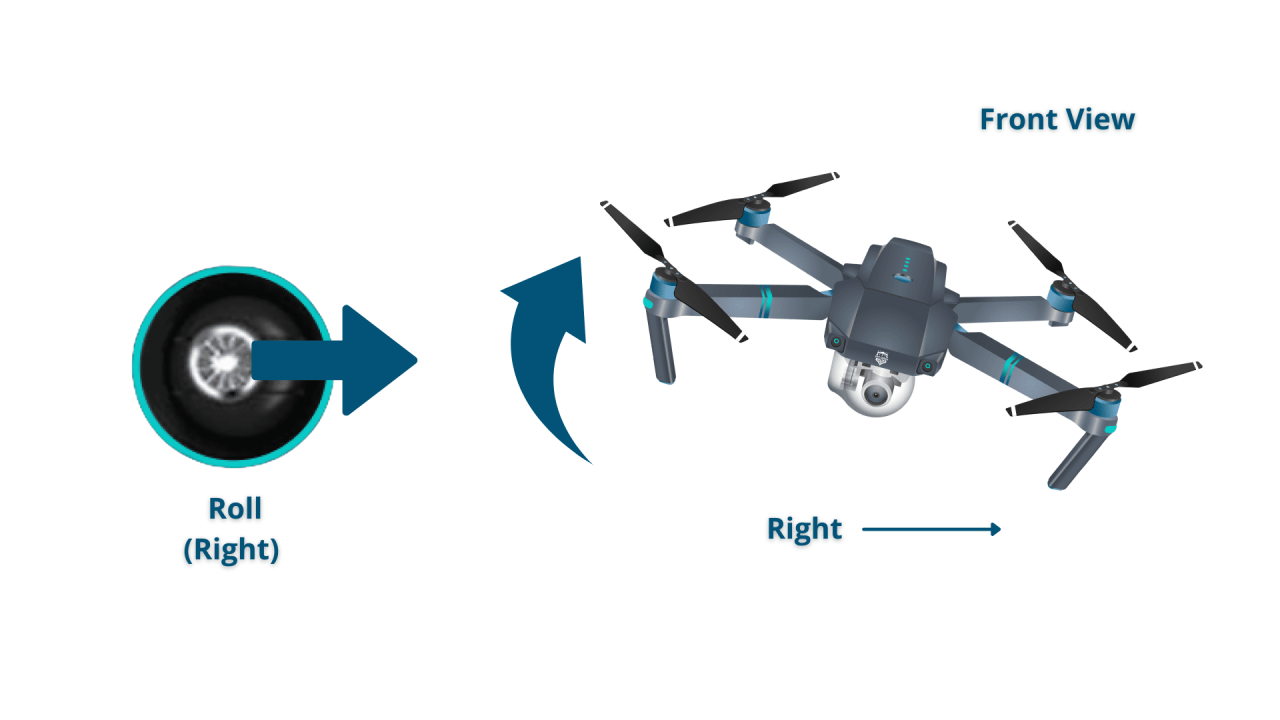
- Roll: Controls left/right movement.
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis (left/right turn).
Advanced Flight Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Advanced maneuvers require practice and skill:
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Circling: Flying in a circular path.
- Precise Positioning: Maintaining a specific location and orientation.
Factors Affecting Drone Stability and Control
Several factors can affect drone stability:
- Wind conditions: Strong winds can make it difficult to control the drone.
- Battery level: Low battery can reduce motor power and stability.
- Radio frequency interference: Interference can disrupt the signal between the controller and drone.
Control Stick Movements and Drone Response
Imagine a typical control stick layout. Pushing the left stick forward moves the drone forward (pitch). Pushing it to the right moves the drone to the right (roll). Pushing the right stick forward increases altitude (throttle), while pushing it to the right rotates the drone right (yaw).
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and techniques. This section details the process.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimizing camera settings is crucial for image quality:
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values result in less noise but require more light.
- Shutter Speed: Controls how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background.
Camera Modes
Different camera modes serve various purposes:
- Photo Mode: For capturing still images.
- Video Mode: For recording video footage.
- Timelapse Mode: For creating time-lapse videos.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
- Choose the right camera settings based on lighting conditions and desired effect.
- Plan your shots and compose your frames carefully.
- Maintain a stable flight for smooth footage.
- Use a gimbal for smoother video.
- Edit your footage to enhance the final product.
Common Camera Settings and Effects
| Setting | Effect on Image/Video |
|---|---|
| High ISO | More noise (graininess), brighter image |
| Low ISO | Less noise, darker image |
| Fast Shutter Speed | Frozen motion, less light |
| Slow Shutter Speed | Motion blur, more light |
| Wide Aperture (low f-number) | Shallow depth of field, blurry background |
| Narrow Aperture (high f-number) | Deep depth of field, sharp foreground and background |
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is essential for maximizing drone flight time and safety. This section Artikels best practices.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
Neglecting battery maintenance can lead to reduced performance, shorter lifespan, and potential safety hazards.
Safe Charging Procedures
- Use the manufacturer-recommended charger.
- Charge in a well-ventilated area.
- Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
- Avoid overcharging.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
Signs of Battery Damage or Degradation
- Swelling or bulging.
- Unusual heat generation during charging or use.
- Reduced flight time.
- Visible damage to the battery casing.
Maximizing Battery Life and Performance
- Avoid extreme temperatures.
- Store batteries at a moderate charge (around 50%).
- Avoid fully discharging batteries.
- Use the manufacturer’s recommended charging and storage practices.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Operating a drone requires adhering to local laws and regulations. This section provides an overview of key considerations.
Key Regulations
Drone laws vary significantly by region. Always research the specific regulations in your area. For example, in many countries, you may need to register your drone and obtain a permit for commercial use. Flight restrictions often exist near airports and sensitive areas.
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use (e.g., commercial vs. recreational), you may need to obtain permits or licenses before flying. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Flight Restrictions
Drones are often restricted from flying near airports, government buildings, and other sensitive areas. Always check for no-fly zones using apps or websites provided by your local aviation authority.
Essential Drone Laws and Regulations Summary
- Register your drone (where required).
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses.
- Adhere to weight and distance restrictions.
- Avoid flying near airports and restricted airspace.
- Maintain visual line of sight.
- Respect privacy laws.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section provides solutions for common drone problems, aiding in quick diagnosis and resolution.
Troubleshooting Guide
- GPS Signal Loss
- Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired. Relocate to an area with better GPS reception. Check for obstructions.
- Motor Malfunctions
- Inspect motors for damage. Check ESCs and connections. Consider replacing faulty components.
- Low Battery Warning
- Initiate RTH (Return to Home). Land the drone immediately. Charge or replace the battery.
- Drone Crash
- Inspect for damage. Review flight logs. Check for potential causes like battery issues, signal interference, or pilot error.
- Controller Not Connecting
- Ensure the drone and controller are properly powered on. Check for interference. Try re-pairing the devices.
- Gimbal Malfunction
- Check gimbal settings. Ensure proper calibration. Look for physical obstructions or damage.
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical understanding, practical skills, and a commitment to safety. This guide has provided a foundational framework for your journey, equipping you with the knowledge to handle your drone responsibly and effectively. Remember that continuous practice and adherence to regulations are crucial for safe and enjoyable drone operation. As you gain experience, explore advanced techniques and push the boundaries of aerial photography and videography, always prioritizing safety and responsible flight practices.
The skies await!
User Queries
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones on the market cater to beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home functionality, and intuitive controls.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’re flying near magnetic interference sources.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If GPS signal is lost, most drones have a “return to home” (RTH) function. If this fails, carefully attempt to manually control the drone back to your location, prioritizing safety.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring you’re well-prepared for a safe and successful flight experience.
Proper drone operation requires practice and adherence to regulations.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight style). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
